IBC syntax
Apr 01, 2025 Andreas Fell
This examples explains the usage of the simplified IBC syntax
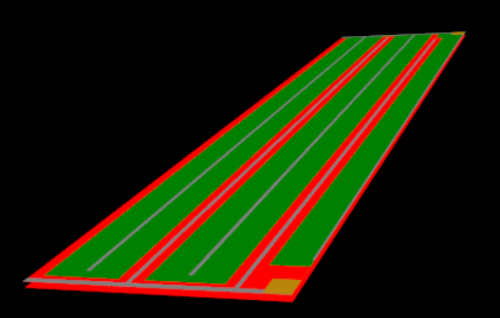
3D view of IBC cell with solder pads
Contained are 4 settingsfiles, showing the 4 different domain types supported by the IBC syntax.
standard
The 'standard' domain type creates a minimal 2D IBC geometry.
busbar-enhanced
Adds finger length and busbar effects to the symmetry domain. This is the best way to optimize finger and busbar pitch, which correctly accounts for finger resistance and busbar-region effects (except for busbar resistance).
pad-enhanced
Adds solder pads and thereby busbar resistance losses to the symmetry domain. This let's you investigate the impact of solder pad placement, including the losses associated with solder pad regions being larger than the busbar width.
multi-domain
Creates a full-cell geometry, which is efficiently solved by applying a numerical mesh only in few subdomains which represent the inner region and the edge regions of the cell. In this domain you can investigate edge and perimeter effects.